-
Keywords"fitting",total
55 records
-
induction brazing copper fittings

Objective Copper ‘tees’ and ‘ells’ are to be brazed to the aluminum body of a refrigeration valveMaterial customer’s valvecopper fittingsbrazeTemperature 2550 F (1400C)Frequency 285 kHzEquipment Power of 15KW induction heating system including a workh…
-
induction brazing brass fitting to copper air lines

Objective To braze brass end-connectors to copper tubes used in aircraft assembly air linesMaterial brass end connectors, copper tubes of different diametersTemperature 1400 F 750CFrequency 350 kHzEquipment Power of 6KW induction heating system, including …
-
induction braze copper tube to brass fitting
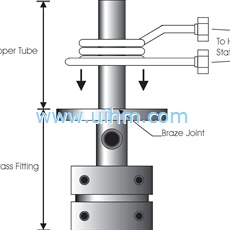
Objective To use induction heating to braze a copper tube to a brass fitting using a preform braze wire. Processing is to occur under an atmosphere of Nitrogen and 4% Hydrogen gas. The braze preforms melt at 1190F, but the parts need to be kept below 1300F…
-
induction brazing steel fitting
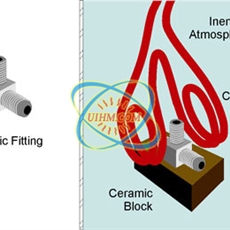
Objective To heat a steel hydraulic hose fitting in an inert atmosphere to 2200F within 7 seconds for brazing without any carbon buildup. Material Three-opening steel hydraulic fitting, pure copper braze paste Temperature 2200F Frequency 273 kHz Equipm…
-
induction shrink fitting

Induction shrink fitting refers to the use of induction heater technology to pre-heat metal components between 150 C (302 F) and 300 C (572 F) thereby causing them to expand and allow for the insertion or removal of another component.Typically the lower te…





